US Government Awards Moderna $176 Million for mRNA Vaccine Development Against H5N1 Influenza
The US government has announced a $176 million funding deal with Moderna to develop an mRNA vaccine against pandemic influenza, specifically targeting the highly pathogenic bird flu virus H5N1. The funding, facilitated through BARDA (Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority), is part of a new Rapid Response Partnership Vehicle (RRPV) Consortium aimed at enhancing the country's preparedness for pandemic threats. Moderna revealed that it has initiated a Phase 1/2 trial of a pandemic influenza vaccine, focusing on H5 and H7 variants of bird flu viruses, with plans to commence a Phase 3 trial in 2025 based on the trial results expected this year. The agreement with Moderna supports the late-stage development of a pre-pandemic vaccine for H5 influenza virus, with provisions for additional vaccine development to address other public health threats.
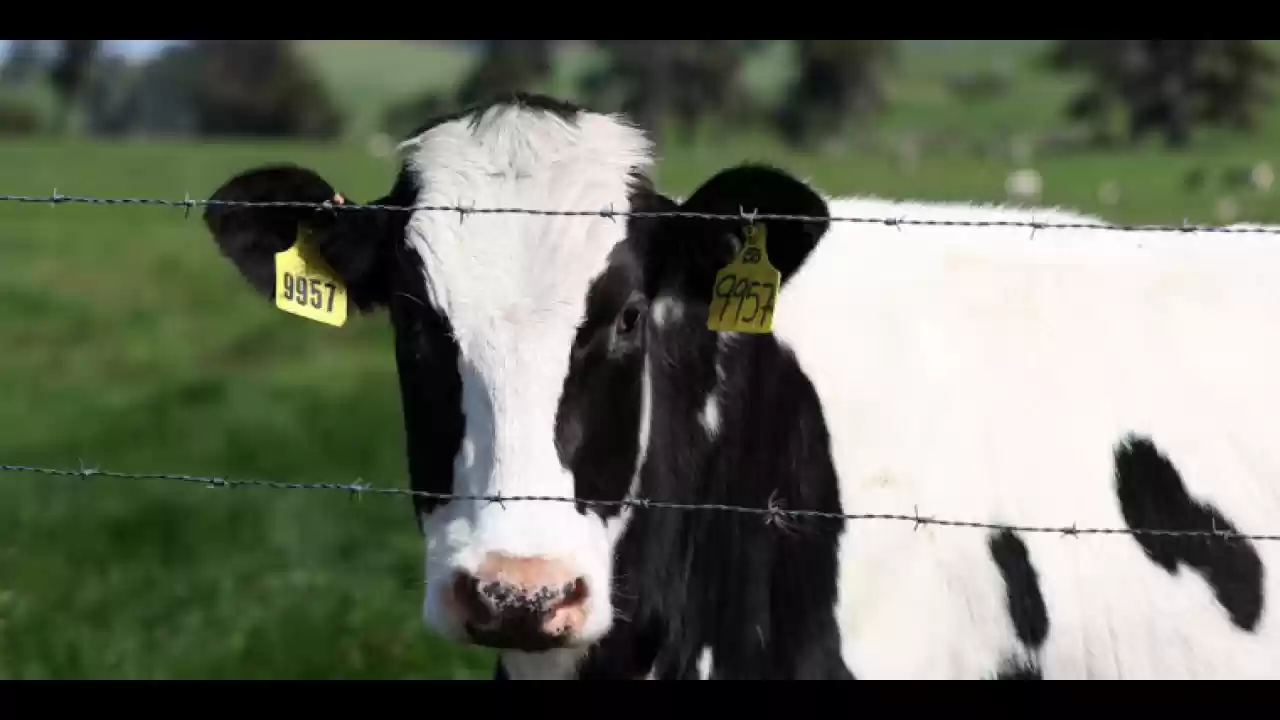
Moderna's CEO emphasized the advantages of mRNA vaccine technology in combating infectious disease outbreaks, citing the success during the COVID-19 pandemic. US health officials have been engaging with Moderna and Pfizer regarding the development of a pandemic bird flu vaccine, which will complement existing protein-based bird flu vaccines. As the H5N1 outbreak among US dairy cattle continues to escalate, concerns are mounting over the country's response. The virus has spread to around 140 herds in 12 states, with some farms hesitating to test for infections, potentially leading to undocumented cases. While the risk to the general public is currently deemed low, farm workers face a higher risk of contracting the virus, with confirmed cases reported in several states.
Criticism has been directed at the US response to the outbreak, with experts highlighting challenges such as resistance from farmers and workers to cooperate with health officials. Federal agencies have introduced assistance programs and biosecurity measures, but voluntary participation remains limited. The movement of cattle and equipment between farms has been identified as a key factor in the virus's spread, prompting regulatory actions to curb transmission. The evolving situation raises concerns about the virus's potential to jump to humans and trigger a pandemic. The funding awarded to Moderna underscores the government's commitment to bolstering pandemic preparedness and leveraging innovative technologies to respond swiftly to emerging infectious disease threats.

 NewsBOT
NewsBOT